You are preparing for front-end, back-end, and full-stack developer interviews. This guide commonly ask question like a what is JavaScript, Event loops, Difference between var, let, and const, closure, hoisting, DOM, Promise, async/await,
event bubbling, difference between == and ===, higher-order functions, difference between map(), filter(), and reduce(), modules and Coding interview questions and answers with example, Definition and Chart with full explanation JavaScript Interview Questions and Answers.
In this blog we will learn the interview question on three level. Experienced developer, Advance, and fresher developer.
JavaScript interview questions and answers for experienced developers
What is JavaScript?
JavaScript is a single threaded async programming language that makes websites interactive. You can use it to handle DOM manipulation. For example, When user click a submit button, It can submit data. Display an alert message, or load new information without refreshing the page.
Let’s explore. Here are our browsers which we use to access websites as a user. Now our browsers understand only HTML, JS and CSS, nothing else. HTML and CSS are purely for displaying the data. They just display static content, nothing else. Now as a user, when you will click on some button or take some action on web page, then it is Javascript which is making the website interactive and dynamic.
JavaScript is a programming language that is used for converting static web pages to interactive and dynamic web pages.
1 . Show a message when a button is clicked
<button onclick="alert('Hello Please Fill the all inputs!')">Click me</button>
2. Changing text on a webpage
<p id="demo-text-chage">Original Text</p>
<script>
document.getElementById("demo-text-change").innerText = "Text changed with JavaScript!";
</script>
Before diving into advanced JavaScript interview questions, we recommend reading our detailed guide on how JavaScript works to strengthen your fundamentals.
What is Hoisting?
Hoisting is a behavior where function and variable declarations are move to top before code runs. Declaration hoist but initialization not hoist. variable and function declarations are moved to memory before code execution.
var is hoisted, You can use it before declaration Its value will be undefined, let is hoisted but You cannot use it before declaration it is throws the error and const is hoisted but You cannot use it before declaration and Value must be assigned at declaration time.
var => hoisted, value = undefined
let => hoisted, but error if used early
const => hoisted, but error if used early and must assigned at declarationWhat is a Closure?
JavaScript inner function remembers and can access variables from its outer function, even after the outer function has finished executing. in sort word Closure is allows to the function remembers and it is a lexical scope.
Help of Closure we can easily manage the data, state, callback function and event handle.
function TeaMachine() {
let cupsServed = 0; // private variable
return function serveTea() {
cupsServed++;
console.log(`Tea served: ${cupsServed} cups`);
};
}
const machine = TeaMachine();
machine(); // Tea served: 1 cups
machine(); // Tea served: 2 cups
machine(); // Tea served: 3 cups
machine(); // Tea served: 4 cups
machine(); // Tea served: 5 cups
machine(); // Tea served: 6 cups
machine(); // Tea served: 7 cups
In this exmple TeaMachine() runs and creates cupsServed and It returns serveTea() Even after coffeeMachine() finishes, serveTea() remembers cupsServed It is called a closure. it is run the seven time and out put is 1 to 7 not 1 seven time.
In React, closures help preserve values across renders without state.
closures are commonly used in middleware, configuration, and data encapsulation in node.js application
Difference Between Primitive and Non-Primitive Data Types?
| Primitive Data Types | Non-Primitive Data Types |
| Number, String, Boolean, Undefine, null are the primitive datatype | Arrays, Objects, Classes, Interfaces, Collections, function, Date are the Non-primitive data type. |
| Primitive data type can store only single value. | Non-Primitive data type ca store multiple values and methods. |
| Primitive data type are immutable. | Non-Primitive data type are mutable. |
| Primitive data type are simple data type | Non-primitive are a complex data type |
Advanced JavaScript interview questions and answers.
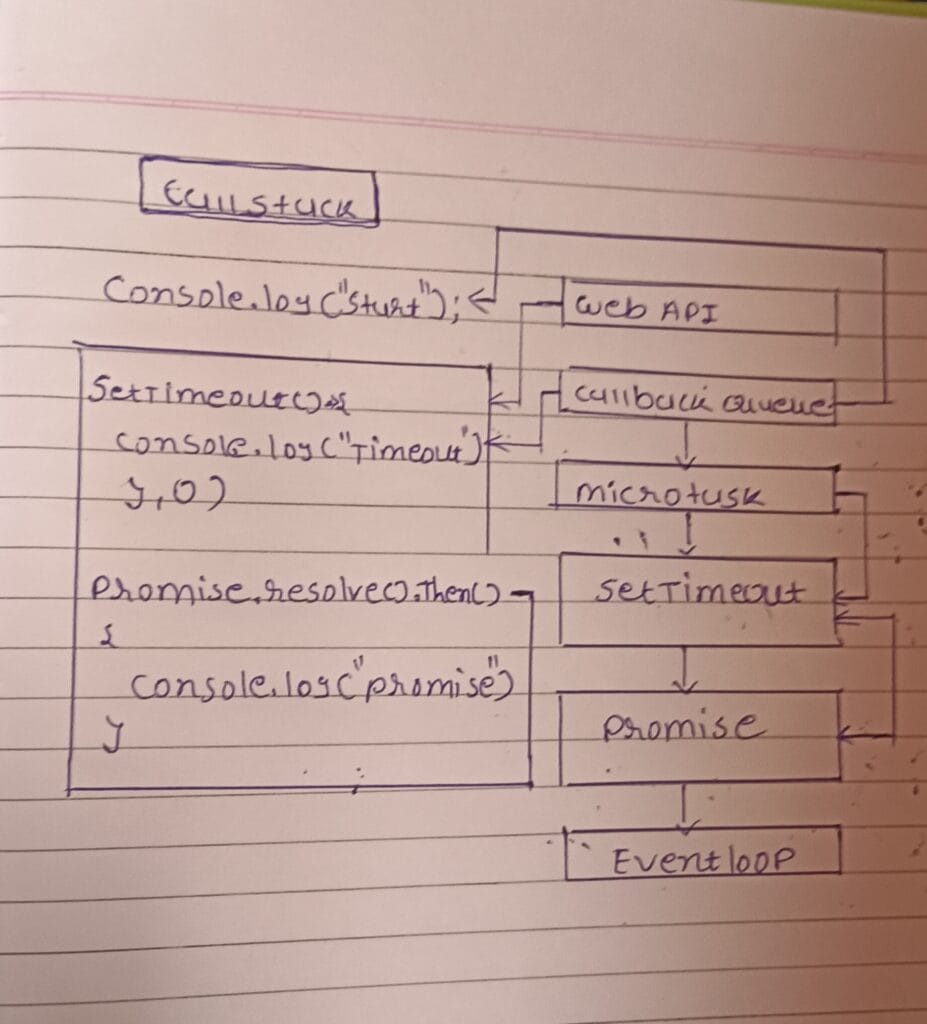
What is Event Loop?
Event loop is a JavaScript mechanism which handle and confirm the asynchronous code like a setTimeout, Promise, async/await and check the call stack is empty then pick the task from queue send to the call stack and if it is a web api then send to the web api.
Event loop working with the Call Stack, Web APIs, Callback Queue (Task Queue), Microtask Queue. Every time event loop check call stack is empty or not. if empty then first execute the Microtask Queue like a Promise.then(), async/await is high priority, and then execute the Callback Queue such as a setTimeout, setInterval.
console.log("Start");
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("Timeout");
}, 0);
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log("Promise");
});
console.log("End");
Start
End
Promise
Timeout
In this example is First execute the Start console.log and Second Execute the End console.log and third execute the Microtask Queue Promise and last execute the Call back Queue TimeOut.
What is a function?
Function is a block of the code that performs a specific task or retunes a value.
function sayHello() {
console.log("Hello!");
}
sayHello(); // Output: Hello!
What is the difference between var, let, and const in JavaScript ?
Var is function-scoped and can be redeclared and updated. Let is a block-scoped (inside the function) it can not be redeclared with in the same scope and it can be updated. const is a block-scoped. can not updated or redeclare. it must be initialized when declare.
| Feature | Using var | Using let | Using const |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Function scoped | Block scoped | Block scoped |
| Redeclaration | Allowed | Not allowed | Not allowed |
| Reassign | Possible | Possible | Not possible |
| Hoisting behavior | Hoisted with undefined | Hoisted (TDZ applies) | Hoisted (TDZ applies) |
| Initialization rule | Initialization optional | Initialization optional | Initialization required |
What is the Difference between == and === in JavaScript interview questions and answers ?
== Operator perform type coercion and convert the string to the number and then compare. and === Operator does not perform type coercion and only set to true if value and type both are same.
5 == "5" // true (string → number)
1 == true // true (true → 1)
0 == false // true (false → 0)
"" == 0 // true ("" → 0)
What are Array Function?
Arrow functions are a shorter way to write JavaScript functions that use the => symbol and automatically share the this value from their surrounding scope. They make code cleaner, faster to write, and easier to read. it one line no need to add the {} and return keyword. it is a implicit return. It is a most important question of the JavaScript interview questions and answers.
const greetUserName= (name) => {
const hour = new Date().getHours();
const message = hour < 12 ? "Good Morning" : "Good Evening";
return `${message}, ${name}!`;
};
console.log(greetUserName("CodeMony"));
Good Morning CodeMony.
What are Callback Function?
A callback function is a JavaScript function that is passed as an argument to the another function. Callback function are used in the iteration, Event handling, Asynchronous operations, Higher-order function and Promises.
function login(username, password, callback) {
if (username === "admin" && password === "1234") {
callback(null, "Login successful");
} else {
callback("Invalid credentials");
}
}
login("admin", "1234", function (error, message) {
if (error) {
console.log("ERROR", error);
} else {
console.log("MESSAGE", message);
}
});
What are asynchronous operations in JavaScript?
JavaScript asynchronous operations are operations that do not block the execution of the code. set Timeout is the asnc function which executes callback function after a period of time. asynchronous operations use on setTimeout, Promises, Data loading from api, file uploads and animation.
console.log("The output will show before setTimeout. ");
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("The code waits for 9 seconds.");
}, 9000);
console.log("The output will show after setTimeout. ");
OUTPUT
The output will show before setTimeout.
The output will show after setTimeout.
The code waits for 9 seconds.
What are promises ?
A Promise in JavaScript is an object that represents the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous operation. and it is way to handle asynchronous operations. Promise has three states: pending, fulfilled, and rejected. It is handled using .then() and .catch() or async/await.
Promise is a represent a value which is not available Yet. but is will be available in feature. and Promises can be in three stage pending, fellfield or rejected.
JavaScript interview questions and answers Promises used for a API calling, File handing, Data fetching, Animation, Event handing.
// Create a function for check age
function checkAge(age) {
// Return promise resolve or reject at list one
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// Compare the age
if (age >= 18) {
C("Access granted");
} else {
reject("Access denied");
}
});
}
// Call the checkAge function
checkAge(27)
.then(msg => console.log(msg))
.catch(err => console.log(err));
// Access granted

In this image function check the age if getter then or equal to 18 it is return a resolve promise and is less then 18 it is return a rejected promise using then() and catch(). it is most important of JavaScript interview questions and answers.
What is JavaScript Reduce?
JavaScript reduce() is an array method used to a combine the large data in to the single value of the data.
reduce param’s are accumulator, current Value and initial value. accumulator is a callback function which is run on every element and store the result. current value is current elements and initial value is staring value of loops.
What is async/await?
async/await is a JavaScript feature that simplifies working with Promises by making asynchronous code easier to read and write with help of the async and await keyword. async is used to declare a function that always returns a Promise. and await is pushed the code executions unit promise resolved or rejected.
JavaScript wait for something to finish and then move on, without stopping the program is called async/await.
Also, Error handling using the try and catch block.
This is a example of the async/await function
function checkPlant() {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("Plant needs water ");
resolve();
}, 1000);
});
}
function waterPlant() {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("Plant watered");
resolve();
}, 2000);
});
}
function celebrate() {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("Happy plant!");
resolve();
}, 500);
});
}
async function careForPlant() {
await checkPlant(); // wait until we know plant needs water
await waterPlant(); // wait until plant is watered
await celebrate(); // then celebrate
console.log("All done ");
}
careForPlant();
Plant needs water
Plant watered
Happy plant!
All done
In this example is it call the first checkPlant() and second waterPlant() and Third celebrate(). it is push the code when check Plant return the promises and same as so on next function.
What is Higher-order function in JavaScript?
Higher-order function is a accept one or more functions as argument(callback fun) and return a function as a result.
//First Example
function hof(func){
func();
}
// Call the func
hof(sayHello);
// Define sayHello function
function sayhello() {
console.log("Hii, Hellow");
}
// Output :- Hil Hellow
//Second Example
function hof(amount, callback) {
if (amount >= 100) {
callback("Recharge successful");
} else {
callback("Recharge failed");
}
}
mobileRecharge(150, function (message) {
console.log(message);
});

JavaScript interview questions and answers for freshers.
What is array ?
Array is a used for store a collection of values, such as a list of numbers or list of names. we can add and remove element to the array using push() and pop(). link
// Create an array
let fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Mango"];
// Use push() to add items at the end
fruits.push("Orange");
fruits.push("Grapes");
console.log(fruits);
// Output: ["Apple", "Banana", "Mango", "Orange", "Grapes"]
// Use pop() to remove item at the end
let removedFruit = fruits.pop();
console.log(removedFruit);
// Output: "Grapes"
console.log(fruits);
// Output: ["Apple", "Banana", "Mango", "Orange"]
const mixed = ["hello", 42, true, { name: "John" }];
console.log(mixed);What is For loop, forEach, filter, substring is the most important JavaScript interview questions and answers.
What Is a JavaScript For Loop?
JavaScript for loops is simple loops is it used for execute the multiple item one by one at a time with write the code manually. There are major three part Initialization, Condition and Increment/Decrements also you can use the break and continue key word for stop loops and skip the elements of iterations.
What Is JavaScript forEach Loop?
JavaScript forEach loop is execute a function each on every elements of an array. forEach is an array method it is only support for JavaScript array. It is not return any value. It is changes on existing array. and It is not support the break or continue. It is use for updating the global variable.
What Is JavaScript substring()?
substring is the use for the extract the characters of the string using the start and end index with the substring() methods. end index is optional. if not pass it is return the until last characters, and it is not support for negative numbers. if pass it is remember as 0 and calculate as staring points.
What is JavaScript filter() method?
In JavaScript filter() is a use for filtering data and it is return a new array with match provided test condition, filter have a three parameter first is element current value of array and Second is an index and third is a array. and it is optional.

1 thought on “JavaScript Interview Questions and Answers (2026) – Complete Guide.”