how JavaScript works in a our computer system Everything in JavaScript happen inside the execution context.
Exaction context is a container. in which have a two part one is a memory components and code components.
Memory components also know as variable environment which is the store memory of declared variable and store the variable with values and function with the key and value pairs.
Code components also known as thread of execution which is execute the single thread, one by one on JavaScript works internally. and execute the code line by in sequence.
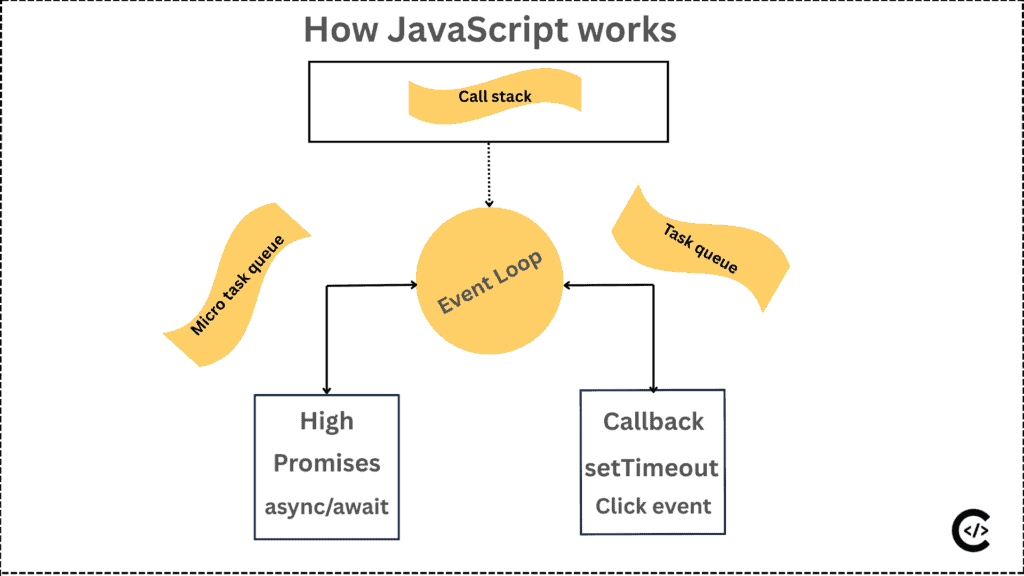
Call Stack, Web APIs, Callback/Task Queue, and Event Loop are the most important parts of how JavaScript works internally.
how JavaScript works with Executing
JavaScript is a single-threaded language. It is working on synchronous sequence.
JavaScript execute the code line by line, for example First line is execute and completed then it is move to the another line is called JavaScript synchronous single threaded language.
Global execution context is assign the all memory components variable as undefined.
Whenever run the JavaScript function that time create a execution context event loop push the context to call stack and call stack execute the context and remove it after complete the task in JavaScript works internally.
JavaScript work with two executions context Global and functions.
let coffee = "Latte";
function makeCoffee() {
let sugar = 2;
console.log(coffee + " with the " + sugar + " spoons of sugar");
}
makeCoffee();
In this example have a Global execution is a coffee and Function execution context is a sugar. coffee variable declare as a global and use on inside a function scop.
how JavaScript works with Call Stack
When executing your JavaScript code, two areas of memory are allocated on the machine, the call stack and the heap. The call stack is designed to be a memory area used to execute your functions. When you call a function, it creates a frame on the call stack which is copy of its local variables.
If you call a function inside a function, it will add another frame to the stack. But if you return from a function, it will pop that frame off the stack.
function wakeUp() {
brushTeeth();
}
function brushTeeth() {
eatBreakfast();
}
function eatBreakfast() {
console.log("Ready for work!");
}
wakeUp();
In this example call stack execute the First wakeUp() then brushTeeth() then eatBreakfast() and after all execution are completed clear the stack.
how JavaScript works with Event Loop
The event loop is JavaScript’s most important controller like a traffic man, It is every time continues checking the call stack is free. If it is free then it moves waiting tasks (like timers or API responses) form the Callback Queue or task queue to the stack. so call stack execute one by one.
Task Queue is a focuses on tasks waiting to execute on the call stack.
Callback Queue is a focuses on callback functions waiting to execute on to the call stack.
console.log("Start JavaScript code");
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("Timeout callback");
}, 0);
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log("Promise callback is a high priority");
});
console.log("End JavaScript code");
Output:
Start JavaScript code.
End JavaScript code.
Promise callback is a high priority.
Timeout callback.
Event loop check the call stack is empty then move the first line Start JavaScript code to the call stack and check again is empty then move the Timeout callback to Call stack and call stack move to the web API.
Event loop check again is empty move the task Promise callback is a high priority to Call stack. Call stack move to web API and event loop check aging and last task End JavaScript code move to Call stack. Call stack execute the task. and Timing task is done to webAPI it is move to the Task queue. event loop check again if task is available then it is move to the Task Call stack. this process is called how JavaScript works. If you have facing any time of problem JavaScript guide.
In this example Execution sequence:-
1) Start JavaScript code.
2) End JavaScript code.
3) Promise callback is a high priority.
4) Timeout callback.
JavaScript execute the first execute normal task then high priority task (micro task) like a
Promises, async/await and then execute the task callback task like a setTimeout.
