JavaScript working with the sting is most common use cases. when if you need the any extract a portion of text on the string. The JavaScript provide the JavaScript substring(). methods. subString() it is usefull for the extract the part of the string with specific start and end index. and end index is a optional. and It is easy to understand and remember syntax. Also, You can use the splice() method we will discuss.
In this blog, We will Learn about the What is JavaScript substring() Method with example, how it works, and syntax with real word example, Advantage of JavaScript substring and Disadvantage. According to the official Mozilla developer substring documentation we will learn JavaScript substring.
substring method in JavaScript is a built in methods so no need to create the extra code just use on your code. First you need to understand how JavaScript work in 2026.
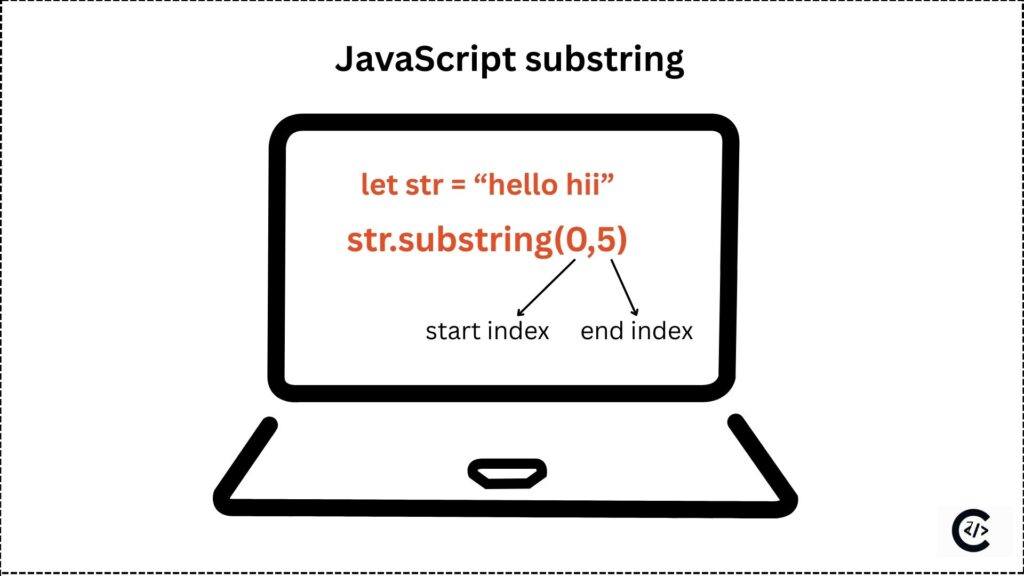
What is JavaScript Substring()?
The substring() methods is use for a extract the characters/part of the provided string, and It is return new string, substring() does not change the original staring, and The substring have a two index start and end. Strat is the starting of string and pickup the the character and end index the the ending of string when stop the pickup end last end index is exclude. If you are new developer you must Learn JavaScript in 2026 with examples.
Why Use the substring() Method?
substring() is an easy to understand. substring is a JavaScript built-in methods no need to extra code just pass the string with require index. It is support on all browser. It is beginner-friendly and simple.
JavaScript Substring() Syntax
Syntax is the most important because we remember the syntax we can use substring on every logical code.
string.substring(startIndex, endIndex)Parameters of substring()
substring
substring is the methods which accept the start and index in params.
startIndex
start Index is the JavaScript substring first parameter and It is starting point of characters extraction
endIndex
end Index is the substring ending parameter which is decide the how to stop extracting of string and it is optimal if not provided it is return the end of the all character start from string index and end with the all last character.
JavaScript substring examples
let text = "You are my friend";
let result = text.substring(0, 10);
console.log(result);Output
You are myIn this example Staring character is the y and end blank space and starting index is 0 and ending index is the 10, but 10 is exclude that way it is the return the You are my.
What substring() in JavaScript
substring in JavaScript is a string function that is use for extract a portion of a string based on passed indexes. is is return a new string without modifying the original one.
How Indexing Works in JavaScript substring()
| Y | o | u | a | r | e | m | y | f | r | i | e | n | d | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
This example is very use full for the best way to understand the index. JavaScript substring is the calculate the space all space have a different index . substring function is understand the space a charector.
Start Index Is Greater Than End Index.
If the Start Index Is Greater Than End Index the JavaScript substring() methods switch the end to start and start to end index.
let text = "Upcoming events ";
console.log(text.substring(14, 3));Output
oming evenIt is switch the end index to start and start index to end internally because the 14 is getter than 3.
Common Mistakes with substring()
There are two common mistake of every developer such as Using Negative Index Values and Confusing substring() with slice().
Handling Negative Values in substring()
Other method allows the negative index but the substring is not allow the negative number on comparison.
it is accept but retune as 0 index. let see with example.
let text = "Clear roadmap";
console.log(text.substring(-4, 5));Output
CleaIt is showing the output is Clea. We passed index -4 but it is calculate as a 0, so It is starting from 0.
Real-World Use Cases of substring()
We have shown the simple example for better understand so we move to the real word example which is help for the best codding cleaner.
1. Extracting User Data
let email = "codemony@example.com";
let username = email.substring(0, email.indexOf("@"));2. Formatting Output
let date = "2026-01-05";
let year = date.substring(0, 4);3. Shortening Long Text
let description = "JavaScript substring methos real word example";
let shortText = description.substring(5, 20) + "...";In this example first is extract the user name from the email. and Second example is the formatting the year of today date and last Third example the get the sort text of the long paragraph it is useful for the real pregaming.
substring() vs slice() vs substr()
substring() is not support for negative number, slice() is support negative number and substr() was supported but now it is decrypted.
Many developer prefer JavaScript substring() to slice() because slice is support for negative number. Once you understand substring, you should learn array methods like JavaScript forEach(), filter(), and reduce().
javascript substr vs substring
There are the key difference of the javascript substr vs substring.
| Feature | substring | substr |
| Syntax | substring(start, end) | substr(start, length) |
| Parameter | end is return end index | length is return character count |
| Example | “abcdef”.substring(1, 4); // “bcd” | “abcdef”.substr(1, 4); // “bcde” |
| Negative values | “abcdef”.substring(-2, 3); // “abc” | “abcdef”.substr(-3, 2); // “de” |
| Standard status | ECMAScript standard | deprecated / legacy |
| Argument auto-swap | swaps if start > end | does not swap |
Does substring() change the original string?
No, It is return the new string.
Is substring() beginner-friendly?
Yes, It is easy to understand.
How does substring() behave with negative numbers?
Any negative value is treated as 0.
Is substring() supported in all browsers?
Yes, It is supported in all browsers,
Is substr() deprecated in 2026?
Yes, it is deprecated in 2026, you can use the substring js.
